Introduction
Cardio, short for cardiovascular exercise, is any physical activity that increases your heart rate and improves the efficiency of your cardiovascular system. It primarily engages the heart, lungs, and circulatory system, helping the body utilize oxygen more effectively during sustained physical activity.
Regular cardio exercise plays a crucial role in overall health and fitness. It aids in weight management, strengthens the heart and lungs, improves endurance, and lowers the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease and diabetes. Beyond physical health, cardio is also known to enhance mood and mental well-being by releasing endorphins, often referred to as “feel-good” hormones.
This blog will explore what cardio is, the different types of cardiovascular exercises, their benefits, and expert recommendations on how much cardio is needed for optimal health.
1. What is Cardio?
Cardio, or aerobic exercise, refers to any form of movement that requires increased oxygen intake over a prolonged period. It stimulates the heart and lungs, making them work harder to supply oxygen-rich blood to the muscles. This process improves cardiovascular endurance and overall fitness.
Some common forms of cardio exercise include:
- Running – A high-impact exercise that significantly elevates heart rate and builds endurance.
- Cycling – Engages lower body muscles while providing an effective cardiovascular workout.
- Swimming – A full-body, low-impact workout that improves cardiovascular fitness while being easy on the joints.
- Brisk Walking – A moderate-intensity exercise that enhances heart health without excessive strain.
- Dancing – A fun and engaging way to improve cardiovascular endurance while enhancing coordination.
- Group Fitness Classes – Structured workouts, such as aerobics or Zumba, that provide guided cardio training in an energetic setting.
The primary function of cardio is to strengthen the heart and lungs, improving blood circulation and oxygen delivery to the muscles. Over time, regular cardiovascular exercise enhances endurance, supports metabolic function, and helps the body perform daily activities with greater ease.
2. Benefits of Cardio
Cardio exercise offers a wide range of health benefits, making it an essential part of any fitness routine. Here’s how incorporating regular cardiovascular workouts can positively impact your body and mind:
- Weight Management – Cardio helps burn calories, making it an effective tool for maintaining or losing weight. When combined with a balanced diet, it can prevent obesity and promote a healthy metabolism. The CDC recommends at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise per week to support weight maintenance.
- Heart Health – Engaging in cardiovascular activities strengthens the heart muscle, improves circulation, and lowers blood pressure. Regular cardio workouts reduce bad cholesterol (LDL) while increasing good cholesterol (HDL), lowering the risk of heart disease and stroke.
- Mental Health – Aerobic exercise releases endorphins, chemicals in the brain that act as natural mood boosters. This helps reduce stress, anxiety, and symptoms of depression, improving overall mental well-being.
Increased Longevity – Studies show that individuals with higher levels of cardiovascular fitness have a lower risk of mortality from diseases such as heart disease and cancer. Cardio enhances overall physical resilience, leading to a longer, healthier life.
Also Read: Can Cardio Burn Fat?
3. Types of Cardio Exercises
Cardio exercises come in various forms, catering to different fitness levels and goals. Choosing the right type can help you stay consistent and enjoy the benefits of cardiovascular training.
- Low-Impact Cardio – Ideal for beginners or those with joint issues, low-impact exercises provide cardiovascular benefits without excessive strain. Examples include:
- Walking
- Swimming
- Elliptical workouts
- Walking
- High-Intensity Cardio – These exercises push the cardiovascular system to work harder in shorter bursts, leading to faster improvements in endurance and calorie burn. Examples include:
- Running
- Vigorous cycling
- Jump rope workouts
- Running
- Circuit Training – This combines strength training with cardio movements for a full-body workout, maximizing calorie burn while building muscle. A typical circuit might include:
- Burpees
- Jump squats
- Push-ups followed by short sprinting bursts
- Burpees
By incorporating a mix of these cardio exercises into your routine, you can optimize cardiovascular health, improve endurance, and maintain long-term fitness.
4. How Much Cardio Do You Need?
The amount of cardio needed varies depending on individual fitness levels and goals, but health organizations provide general guidelines to ensure optimal cardiovascular benefits.
- General Recommendations (CDC Guidelines):
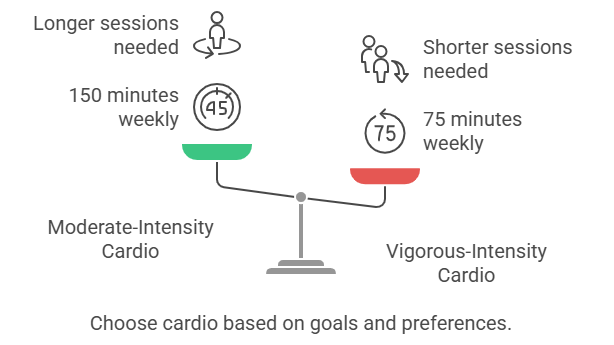
- Moderate-Intensity Cardio: At least 150 minutes per week (e.g., brisk walking, light cycling).
- Vigorous-Intensity Cardio: At least 75 minutes per week (e.g., running, fast-paced cycling).
- These can be broken into smaller sessions, such as 30 minutes per day, five days a week, for consistency and sustainability.
- Moderate-Intensity Cardio: At least 150 minutes per week (e.g., brisk walking, light cycling).
- Tailoring to Individual Needs:
- Beginners may start with shorter, lower-intensity sessions and gradually increase duration and intensity.
- Athletes or those with specific fitness goals may require longer or more intense cardio sessions for endurance and performance.
- Beginners may start with shorter, lower-intensity sessions and gradually increase duration and intensity.
People with health conditions should consult a professional to create a safe and effective cardio plan.
5. Conclusion
Cardio is a fundamental component of a healthy lifestyle, benefiting the heart, lungs, metabolism, and mental well-being. Regular cardiovascular exercise supports weight management, heart health, mental clarity, and longevity.
To make cardio sustainable and enjoyable, individuals should choose activities they enjoy—whether it’s walking, swimming, dancing, or high-intensity interval training (HIIT). Incorporating different forms of cardio ensures variety and keeps workouts engaging.
Before beginning a new exercise regimen, it’s always best to consult a healthcare provider, especially for individuals with pre-existing conditions or those new to fitness. By integrating cardio into daily life, anyone can take significant steps toward better health and overall fitness.
FAQs About Cardio
- Is cardio necessary for weight loss?
Yes, cardio helps burn calories and supports weight loss when combined with a balanced diet. However, strength training and a proper nutrition plan also play a crucial role. - How often should I do cardio exercises?
The CDC recommends at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity cardio per week. You can adjust based on your fitness level and goals. - Can I do cardio every day?
Yes, but it’s important to listen to your body and allow recovery time, especially after high-intensity sessions. Low-impact activities like walking or swimming can be done daily. - What’s the best type of cardio for beginners?
Walking, swimming, and cycling are great low-impact options for beginners. Gradually, you can increase intensity as your endurance improves. - Should I do cardio before or after strength training?
It depends on your goal. If building strength is your priority, do weight training first. If improving endurance is your focus, start with cardio.

